
When price moves down to a moving average line or up to a moving average line, traders can use this as a signal that price might stop or retrace at that point.įor example, if price moved down to the 200EMA a trader might think that price might stop moving down from there as the 200 EMA will act as support for price to move back up. Moving averages are often used to compare where the current price of the underlying instrument is in relation to support and resistance on a chart. Other moving averages are basically an EMA that assigns different weighting and smoothing variables to the calculations. While there are other more complicated moving average calculations beyond EMA and SMA, these two are the most common. You just need to pick a starting value for the EMA calculation.Īs with simple moving averages, no calculation is needed on your part, the moving average indicator will calculate this for you and show the results as a line on your chart. Note the first day of the EMA calculation can either start with yesterday’s closing price or the SMA from yesterday. Calculate the EMA = (Price today x Multiplier) + (EMA yesterday x ( 1 – multiplier) Using price, the multiplier (time period) and the previous EMA value.ġ. Determine the SMA or use yesterday’s closing price to beginģ.
#Ema meaning in stocks series#
This makes them more responsive to changes in price and also acts in smoothing out the line.Įxponential moving averages calculate the average of a series of numbers using a weighting multiplier that typically assigns more weight to later data. Simple moving average = sum of closing prices divided by number of daysĮxponential moving averages assign more influence on recent numbers and less on old data because of a weighting variable in the calculation.
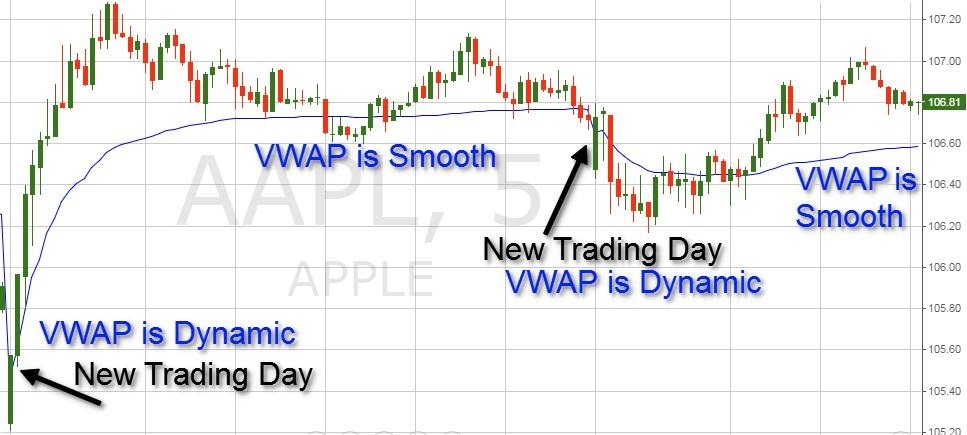
Traders might have multiple moving averages on their charts at one time and use different lines to represent different actions you might take with your trades Simple Moving AverageĪ simple moving average, the most basic of moving averages, is calculated by summing up the closing prices of the last x days and dividing by the number of days.įor example, if WTI (CL) contract closed at $45.50, $45.25 and $46.10 over the last three days the moving average would be calculated as follows: These moving averages will appear on a chart as a line above or below price.

Two common moving average calculations are simple moving averages and exponential moving averages. Each method will come up with a slightly different result and place emphasis on a certain section of the data being calculated. There are a number of ways to mathematically calculate the average of a set of numbers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
